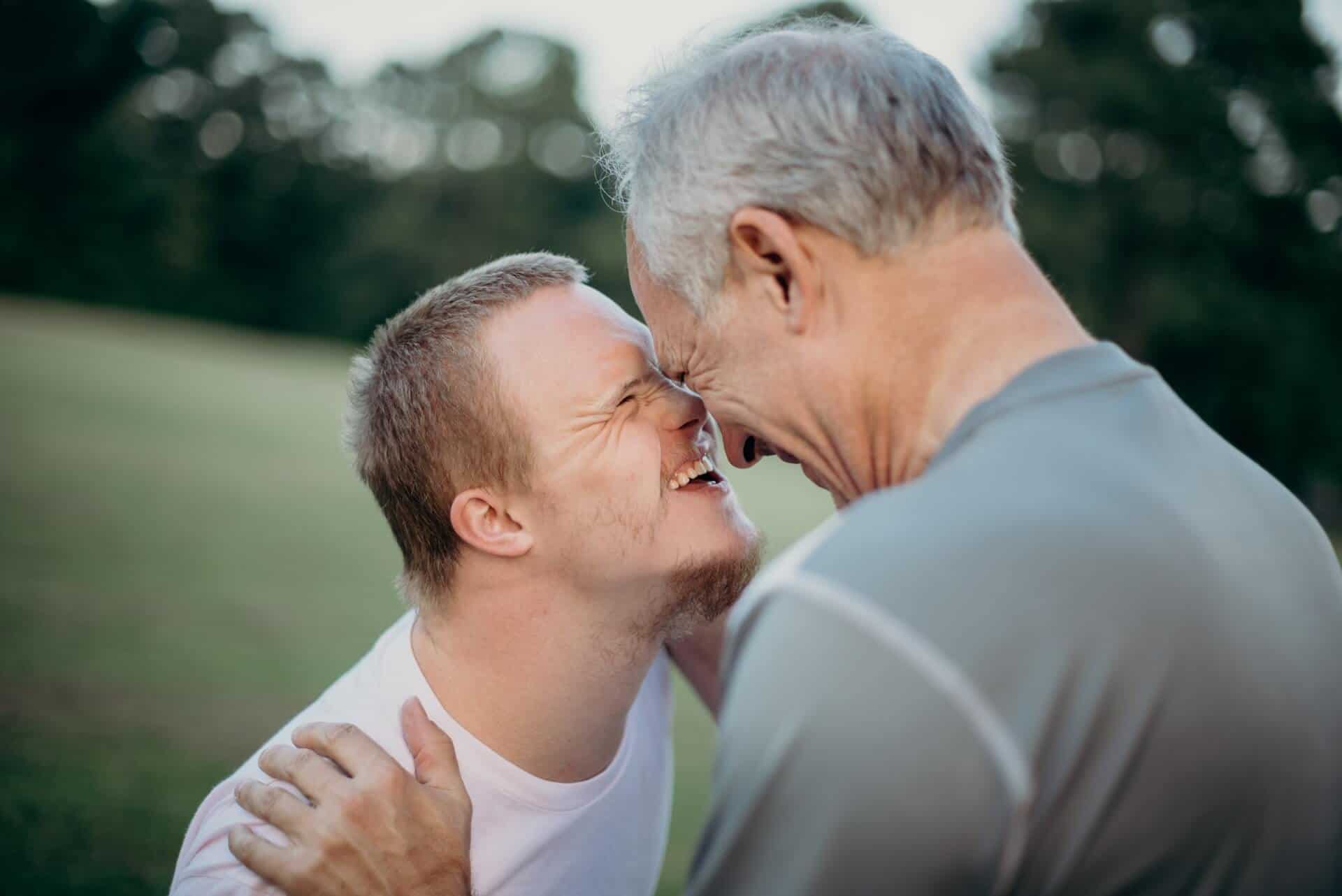
Down’s syndrome is a condition in which chromosome 21 is duplicated, resulting in three copies rather than just two. It is associated with intellectual, developmental, and physical changes.
The eyes are one component and there are a variety of conditions that individuals diagnosed with Down syndrome may be affected by or more susceptible to. Read on to learn about some of the most common ocular findings.
Refractive Error and Glasses
This refers to an individual’s prescription in corrective eyewear such as glasses or contact lenses in order to see as clearly as possible. Patients with Down syndrome are more likely to need corrective eyewear whether for nearsightedness, farsightedness, or astigmatism.
Strabismus is a Common Feature in Down Syndrome
Strabismus refers to an eye turn that the individual may have. This could be one eye turning in and out, or both eyes turning and switching back and forth. It could also be present at all times or only at some points in the day and associated with certain activities.
An eye more often turns inward, but in either case amblyopia or lazy eye may develop. This means that because the turned eye is not being used as frequently, it will not receive as much visual stimuli and its pathways to the brain will not fully develop, leading to permanent vision reduction in that eye if the eye turn is not fixed in childhood.
Down’s Syndrome Can Cause Keratoconus
At the very front of the eye is the clear cornea, which is thinned in this condition, causing the fluid from inside the eye to push outwards. This causes the cornea to bulge outwards into a cone shape and distorts the curvature, affecting vision. This condition has been shown to be associated with eye rubbing and our optometrist will check to make sure that there are no underlying causes inducing this.
Cataracts
A cataract refers to the clouding of the lens within the eye, causing blurry vision or a spot in vision. If noted, our optometrist will assess to see how severe the cataract is and, if needed, refer the patient to receive surgical treatment to replace the lens. Patients with Down syndrome are at higher risk for either congenital cataracts (present at birth) or developing cataracts as they age earlier than the general population.
Glaucoma
This is a group of disorders that refer to the death of the nerve cells at the back of the eye, which are responsible for providing peripheral vision. This is often associated with higher eye pressure but this is not the only variable.
Treatment includes eye drops, instilled everyday, to lower eye pressure or certain laser procedures that help with outflow of the fluid within the eye to lower the pressure. Individuals with Down syndrome are at higher risk for higher eye pressures and glaucoma.
Blepharitis
This is a condition that leads to inflammation of the eyelids and the glands within them. It is often associated with a dry or burning feeling in the eyes and redness. Eyelid hygiene is an important component for this condition and it can be treated with eyelid cleaning, warm compresses, steroids, or antibiotics.